The Zika virus is likely to spread across nearly all of the Americas, the World Health Organization has warned.
The infection, which causes symptoms including mild fever, conjunctivitis and headache, has already been found in 21 countries in the Caribbean, North and South America.
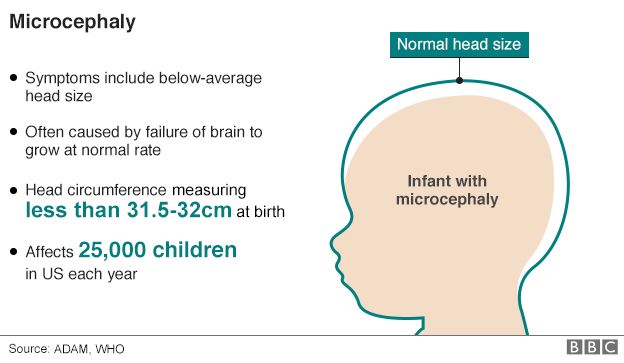
It has been linked to thousands of babies being born with underdeveloped brains and some countries have advised women not to get pregnant.
No treatment or vaccine is available.
The virus is native to Africa and was first found to be spreading in the Americas in Brazil in May 2015.
The lack of any natural immunity in the Americas is thought to be helping the infection to spread rapidly.
Countries with confirmed cases of Zika virus

Mosquito
Zika is transmitted by the bite of Aedes mosquitoes, which are found in all countries in the region except Canada and Chile.
In a statement, The Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), the regional office of the WHO, said: "PAHO anticipates that Zika virus will continue to spread and will likely reach all countries and territories of the region where Aedes mosquitoes are found."

It also confirmed the virus had been detected in semen and there was "one case of possible person-to-person sexual transmission" but further evidence was still needed.
Around 80% of infections do not result in symptoms.
But the biggest concern is the potential impact on babies developing in the womb. There have been around 3,500 reported cases of microcephaly - babies born with tiny brains - in Brazil alone since October.
PAHO warned pregnant women to be "especially careful" and to see their doctor before and after visiting areas affected by the virus.
Colombia, Ecuador, El Salvador and Jamaica last week recommended women delay pregnancies until more was known about the virus.
Although officially PAHO says "any decision to defer pregnancy is an individual one between a woman, her partner and her healthcare provider".
Maria Conceicao Queiroz said there was a sense of fear where she lives near the Olympic Park in Rio de Janeiro: "Every one is at risk, we're all scared of getting Zika.
"We're surrounded with dirty water, polluted water, but what can we do but put repellent on, to try to keep the mosquitoes away."
Global threat
Prof Laura Rodrigues, a fellow of the Brazilian Academy of Sciences and from the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, said some data suggested that up to one-in-fifty babies had birth defects in one of the worst hit areas - Pernambuco state in Brazil.
She said: "Until November we knew nothing, this has caught us by surprise and we're trying to learn as fast as we can.
"Wherever there is dengue, there is mosquito, then it will spread and not just in Americas I think there is a very real chance it will spread in Asia."
Latest Stories
-
JoyNews poll: Akufo-Addo, his government’s ‘killer’ taxes and nepotism blamed for NPP’s 2024 defeat
58 minutes -
Barca scores 5 again in Copa del Rey win over Betis
2 hours -
Harry Kane scores again as Bayern thrash Hoffenheim
2 hours -
Arsenal win North-London derby to close gap at the top
2 hours -
Djokovic breaks Federer record in Melbourne win
3 hours -
Foreign Affairs Ministry lists categories of recalled diplomatic and service passports
3 hours -
NAELP refutes defamatory claims, highlights achievements
4 hours -
2024 Election: Voter apathy caused NPP’s defeat – Justin Kodua
4 hours -
Ghanaian teacher shortlisted for GEM’s $1m global prize
4 hours -
Young entrepreneurs encouraged to capitalise on 5-year tax exemption Incentives
4 hours -
Lord Morrgan fulfils promise; gifts fan Wale new motorbike
5 hours -
CHAN 2024 Draw: Two-time Champions Morocco in Group A with hosts Kenya
5 hours -
Disregarding ORAL’s mandate doesn’t help the nation – Kpebu
5 hours -
NDC gov’t cannot fulfil its promises under the current IMF programme – Godfred Bokpin
5 hours -
13 newly recruited staff posted to Creative Arts Agency
5 hours

