Audio By Carbonatix
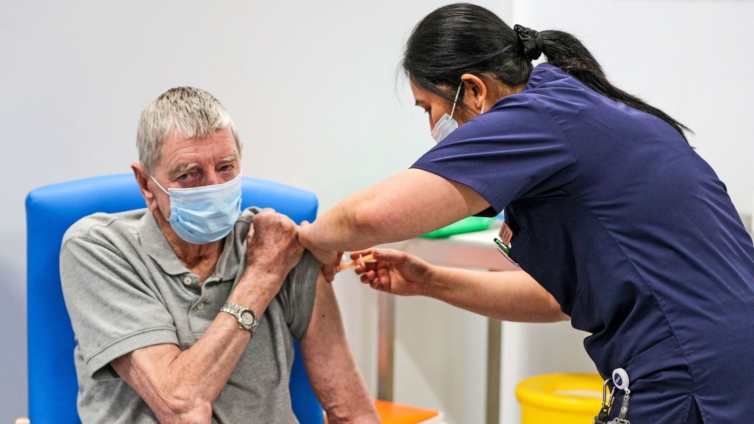
The risk of developing a blood clot after having Covid-19 is eight times higher than after being given the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine, according to a study by Oxford University.
Cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT) occurred in 39 in a million Covid-19 patients, compared with about five in a million people given the AstraZeneca jab.
In the study of over 500,000 coronavirus patients, the risk was reported to be around 100 times higher than normal after infection.
Numerous countries have limited the use of the vaccine to certain age groups or paused its rollout - with Denmark even dropping the jab from its vaccination programme permanently - following reports of very rare cases of blood clots.
The UK's medical regulator has said the vaccine is still safe and effective but has limited its use in those under 30 as this age group is less at risk of becoming seriously ill with coronavirus.
However, the Oxford study suggested around a third (30%) of the CVT reports after Covid-19 infection were in people under 30.
Scientists have said the technology used in the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine, harnessing an adenovirus, has been linked to a slightly increased risk of blood clots.
It's the same explanation for the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, which has been paused in the US after a handful of clotting reports there.
In over 480,000 people who received the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines, which use mRNA technology instead, CVT occurred in about four in a million people.
The risk of developing CVT after taking either of these vaccines is about 10 times lower than after being infected with coronavirus, the study suggests.
But the researchers said comparisons should be interpreted with caution because data is still being gathered.
Professor Paul Harrison, from the University of Oxford, said: "We've reached two important conclusions. Firstly, Covid-19 markedly increases the risk of CVT, adding to the list of blood clotting problems this infection causes.
"Secondly, the Covid-19 risk is higher than seen with the current vaccines, even for those under 30; something that should be taken into account when considering the balances between risks and benefits for vaccination."
And Professor Sir John Bell, the university's regius professor of medicine, told Sky News: "The best way if you want to have a bad clotting problem, is to get Covid.
"And if you don't get a vaccine you're going to get Covid, and if you get Covid you'll have a very, very much higher risk of getting a bad clotting problem.
"So, the clotting problems of the vaccine are pretty trivial compared to the real risks of getting clotting problems if you get Covid."
Latest Stories
-
‘Adom FM’s Strictly Highlife’ lights up La Palm with a night of rhythm and nostalgia
3 minutes -
Ghana is rising again – Mahama declares
5 hours -
Firefighters subdue blaze at Accra’s Tudu, officials warn of busy fire season ahead
5 hours -
New Year’s Luv FM Family Party in the park ends in grand style at Rattray park
5 hours -
Mahama targets digital schools, universal healthcare, and food self-sufficiency in 2026
6 hours -
Ghana’s global image boosted by our world-acclaimed reset agenda – Mahama
6 hours -
Full text: Mahama’s New Year message to the nation
6 hours -
The foundation is laid; now we accelerate and expand in 2026 – Mahama
6 hours -
There is no NPP, CPP nor NDC Ghana, only one Ghana – Mahama
6 hours -
Eduwatch praises education financing gains but warns delays, teacher gaps could derail reforms
6 hours -
Kusaal Wikimedians take local language online in 14-day digital campaign
7 hours -
Stop interfering in each other’s roles – Bole-Bamboi MP appeals to traditional rulers for peace
8 hours -
Playback: President Mahama addresses the nation in New Year message
8 hours -
Industrial and Commercial Workers’ Union call for strong work ethics, economic participation in 2026 new year message
10 hours -
Crossover Joy: Churches in Ghana welcome 2026 with fire and faith
10 hours