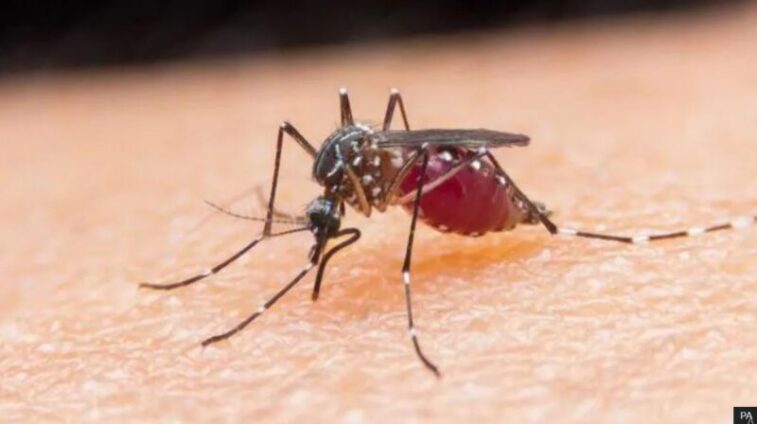
Scientists believe they have found a quirky way to fight mosquito-spread diseases such as dengue, yellow fever and Zika - by turning male insects deaf so they struggle to mate and breed.
Mosquitoes have sex while flying in mid-air and the males rely on hearing to chase down a female, based on her attractive wingbeats.
The researchers experimented, altering a genetic pathway that male mosquitoes use for this hearing. The result - they made no physical contact with females, even after three days in the same cage.
Female mosquitoes are the ones that spread diseases to people, so trying to prevent them from having babies would help reduce overall numbers.
The team from the University of California, Irvine studied Aedes aegypti mosquitoes, which spread viruses to around 400 million people a year.
They closely observed the insects' aerial mating habits - which can last between a few seconds to just under a minute - and then figured out how to disrupt them using genetics.
They targeted a protein called trpVa that appears to be essential for hearing.
In the mutated mosquitoes, neurons normally involved in detecting sound showed no response to the flight tones or wingbeats of potential mates.
The alluring noise fell on deaf ears.
In contrast, wild (non-mutant) males were quick to copulate, multiple times, and fertilised nearly all the females in their cage.
The researchers from the University of California, Santa Barbara, who have published their work in the journal PNAS, said the effect of the gene knock-out was "absolute", as mating by deaf males was entirely eliminated.
Dr Joerg Albert, from the University of Oldenburg in Germany, is an expert on mosquito mating and I asked him what he made of the research.
He said attacking sense of sound was a promising route for mosquito control, but it needed to be studied and managed.
"The study provides a first direct molecular test, which suggests that hearing is indeed not only important for mosquito reproduction but essential.
"Without the ability of males to hear - and acoustically chase - female mosquitoes might become extinct."
Another method being explored is releasing sterile males in areas where there are pockets of mosquito-spread diseases, he added.
Although mosquitoes can carry diseases, they are an important part of the food chain - as nourishment for fish, birds, bats and frogs, for example - and some are important pollinators.
Latest Stories
-
Tamale Teaching Hospital achieves 28% reduction in maternal mortality
1 hour -
Teacher in court for stealing, defrauding by false pretence
2 hours -
Amanda Akuokor Clinton writes: Why Ghana recently failed to renegotiate the IMF deal
3 hours -
Ningo-Prampram MP secures assurance of improved water supply from Ghana Water Company
4 hours -
Anglogold Ashanti intervenes amidst surge in kidney cases in Obuasi
4 hours -
‘Mic On, Barriers Off’: JoyNews documentary explores what media freedom means to persons with disabilities
4 hours -
US farmers’ delegation visits Ghana to strengthen agricultural collaboration
4 hours -
Ghana at risk of not passing IMF fourth review in April
4 hours -
Kurt Okraku’s ExCo feat: A moment worth celebrating, not tearing down
5 hours -
Abossey Okai spare parts dealers deny claims of price hikes transport fare increase
6 hours -
Kobina Ansah’s The Saint In The Devil’s Shoes has only one character
6 hours -
Fifty-one dead after North Macedonia nightclub fire
6 hours -
Voice of America channels fall silent as Trump administration guts agency and cancels contracts
14 hours -
Cybersecurity awareness initiative equips students with essential digital skills
15 hours -
Government’s proposed 80% transfer of mineral royalties sparks controversy
15 hours