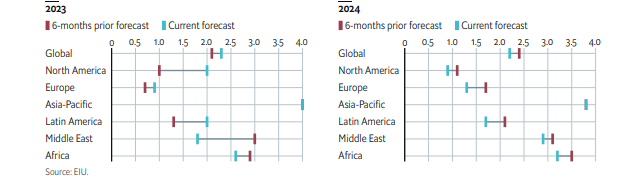
Global growth is forecast to be stable, despite higher interest rates, avoiding contraction.
According to The Economist Intelligence Unit, the lagged impact of a broad rise in interest rates will constrain global economic activity in the remainder of 2023 and in 2024, but there are no indications of systemic strain in debt markets that could pull the world economy into a painful contraction.
“We forecast that US growth will slow significantly in 2024, but will avoid a recession, and some momentum will build in Europe as German industry normalises following energy-related disruptions. Moderate stimulus in China will inject sufficient momentum behind its economy to preserve expansion, while other emerging markets will benefit from reduced uncertainty that will come with the conclusion of global monetary tightening”.
“We forecast that global economic growth will decelerate to 2.2% (at market exchange rates) in 2024, from an estimated 2.3% in 2023. The outlook improves in subsequent years (we forecast growth of 2.7% a year on average in 2025-28) aided by the onset of monetary easing and increased funding for investment in technology and the energy transition”, it added in its latest Global Economic Outlook.
Africa is expected to grow at a rate of about 2.9% in 2023 and 3.5% in 2024.
Disinflation process to continue
It also forecasts that disinflation will continue, with risks weighted to the upside.
“The supply-side shocks that drove price increases in 2021-22 will reverse as supply-chain dislocation eases. This will drive inflation lower in most markets (we forecast that it will average 2.4% across developed economies in 2024), if not undo the rapid price gains of recent years”, it explained.
However, it said risks to the inflation outlook are skewed to the upside, adding, a widening of the Israel-Hamas war that disrupted oil supply would drive up hydrocarbon prices, and stronger than expected effects from El Niño climate conditions on agriculture production would push up food prices in 2024, especially in developing economies.
Also, there is a moderate risk that demand will prove more resilient than we expect in developed markets.
Latest Stories
-
Too many Ghanaian businesses continue to price in US dollars – BoG Governor
3 minutes -
Cedi rising; Ghana must rise too – BoG Boss
6 minutes -
Emmanuel Wie-Addo writes: Tapping into a $1.8tn space economy
15 minutes -
Ghana must shift from raw commodity exports to value-driven growth – Dr Asiama
20 minutes -
Rejecting coins as a means of payment is illegal – BoG warns traders
22 minutes -
BoG intensifies crackdown on counterfeit cedi
24 minutes -
BoG to build efficient, transparent FX market
27 minutes -
BoG finalizes regulatory framework to check cryptocurrency
39 minutes -
BoG considers price hedging programme for gold exports – Governor
45 minutes -
Ghana records GH₵ 4.14b trade surplus – BoG Governor
49 minutes -
We can’t stop cryptocurrency use – BoG
49 minutes -
Cedi appreciation due to strengthened economic fundamentals – BoG Governor
58 minutes -
Use data from BoG to make cedi projections, not predictions from ‘Zamerama’ – Governor Asiama
1 hour -
Retract and apologise for disrespecting our MP – Essikado-Ketan NDC to Afenyo-Markin
1 hour -
APL claims vindication following IMF’s revelation of BoG’s $1.4bn forex support
1 hour

