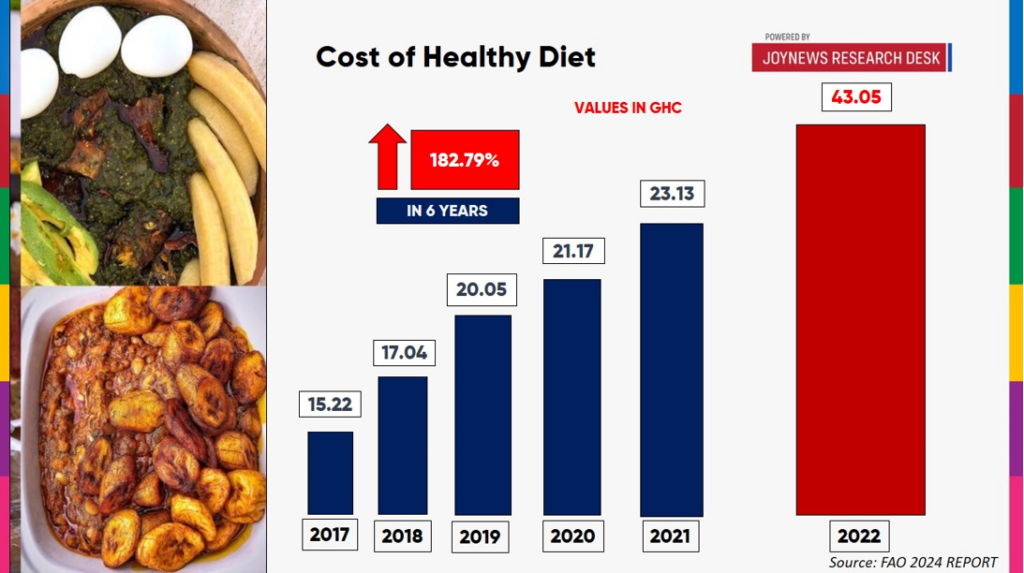
The cost of maintaining a healthy diet in Ghana has seen an alarming rise of almost 200% over the past six years. This is according to the 2024 Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World report.
The FAO defines a healthy diet as one that ensures diversity in food groups, adequacy of essential nutrients, and moderation of harmful ingredients, and balance in energy and macronutrient intake.
This approach supports overall well-being by promoting a varied, nutritious diet while minimizing the risk of chronic diseases.
In Ghana, the cheapest possible healthy diet relies on locally available foods that meet energy and nutritional standards. However, as prices soar, even this basic dietary requirement is becoming increasingly out of reach.
Between 2017 and 2022, the cost of a healthy diet increased from $3.45 to $4.29 per day, equivalent to GHS 15.22 and GHS 43.05, respectively. This 182.79% increase has significantly strained household budgets, making a healthy diet unattainable for many Ghanaians.
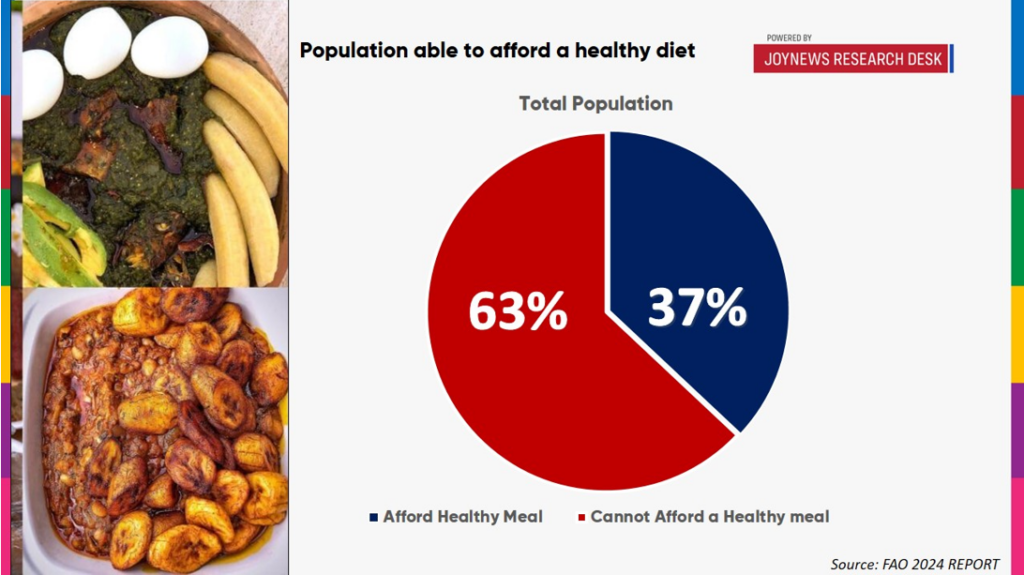
The report reveals that 21.1 million Ghanaians, that is 63% of the population, are unable to afford a healthy meal for a day.
This marks an increase of 1.4 million people since 2017, when 19.7 million faced the same challenge. The data highlights a worrying trend of deepening food insecurity in a country heavily reliant on agriculture yet increasingly vulnerable to global economic shocks.
The report further emphasizes two major events to have exacerbated this crisis. The COVID-19 pandemic disruption to global supply chains, driving up the cost of food and energy. Compounded by the war in Ukraine, which further strained global food supply networks, particularly in grains and fertilizers. As a result, inflationary pressures soared, pushing basic food prices beyond the reach of many households in Ghana.
According to FAO, this budget optimization could enable 4.2 million more Ghanaians to afford a healthy diet by 2025, with the number rising to 5.3 million by 2030 through sustained implementation.
The situation calls for urgent policy measures to improve food affordability and accessibility. The report suggests optimizing Ghana’s agricultural budget by reducing spending on seed subsidies and irrigation while increasing investments in mechanization and extension services. This reallocation aims to enhance Agrifood GDP.
The FAO's 2024 report is a stark reminder of the widening gap between income levels and food affordability, and the pressing need for both national and international interventions to secure the right to adequate nutrition for all Ghanaians.
Latest Stories
-
Cedi appreciation: Gov’t’s expenditure misalignment must be investigated – Gideon Boako
5 minutes -
Ghana needs $562bn for full energy transition by 2070 – Energy Ministry
14 minutes -
Suspended CJ Torkornoo files injunction against committee probing her removal
27 minutes -
Photos: AMA demolishes illegal structures, uncovers ‘Lucifer Village’ on day 2 of decongestion exercise at Circle
46 minutes -
JHS pupil dies in galamsey pit after being chased by security at Pramkuma
1 hour -
AMA uncovers ‘Lucifer Village’ at Nkrumah Circle: Brothels, bars, illegal structures built over gutters
1 hour -
Cedi gains unsustainable without real sector growth – Prof Lord Mensah warns
1 hour -
Otumfuo Osei Tutu II Foundation donates essential equipment to Manhyia Gov’t Hospital
1 hour -
Ghana gets $220m from Newmont’s $1billion Sale of Akyem Mine
2 hours -
First National Bank appoints Adwoa Boateng Addo as Chief People Officer
2 hours -
Trump administration to scrap police reform measures in some US cities
2 hours -
Gatsi, Kwakye, 2 others appointed as advisors to BoG Governor
2 hours -
Gideon Boako questions Goldbod’s $3bn spending overrun
2 hours -
Verified: Bawumia’s claim NDC gov’t has added less than one tonne of gold to reserves true
2 hours -
Don’t Work Ghanaians to Death: Why Raising the Retirement Age to 65 is misguided
2 hours

