The European Commission has proposed tougher controls on Covid vaccine exports after it accused UK-Swedish firm AstraZeneca of failing to honour its contract to supply EU countries.
The plans, to go before EU leaders on Thursday, stop short of a ban but could enflame tensions with the UK.
Any shipment would be assessed on the destination country's rate of vaccinations and vaccine exports.
Meanwhile, millions of AZ doses have reportedly been found in Italy.
La Stampa website says some 29 million vaccine doses due to be shipped to the UK were being stored at the Catalent plant in Anagni near Rome but were discovered by Italian inspectors as part of an investigation by the European Commission.
Italian military police did not deny the raid took place, but when asked by the BBC about the report, the foreign ministry in Rome and the Italian prime minister's office refused to comment.
The plant has a contract with AstraZeneca to "fill and finish" its vaccines and is set to do the same for the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, also approved for use in the EU.
The reported discovery comes weeks after the Italian government blocked the export of 250,000 doses of the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine to Australia, as part of new EU regulations allowing a shipment to be stopped if a company is seen as failing to meet its obligations to the 27 member states.
The latest EU proposals are aimed at securing vaccine supplies. When asked whether the aim was to punish the UK in particular, EU Health Commissioner Stella Kyriakides said: "We're dealing with a pandemic and this is not seeking to punish any countries."
As infections rise across Europe, member states are trying to speed up Covid vaccination campaigns after a sluggish start, blamed partly on delayed deliveries of the AZ drug as well as safety checks.
Germany had announced a strict five-day lockdown over Easter, but in a dramatic announcement on Wednesday Chancellor Angela Merkel called it off after talks with state leaders. "This mistake is my mistake alone," she said, explaining that it had been decided with the best of intentions.
Italian Prime Minister Mario Draghi said on Wednesday that on average 170,000 daily vaccinations had been carried out this month and that the objective was to increase that to half a million. He highlighted the large number of sites and people taking part in the UK vaccination drive.
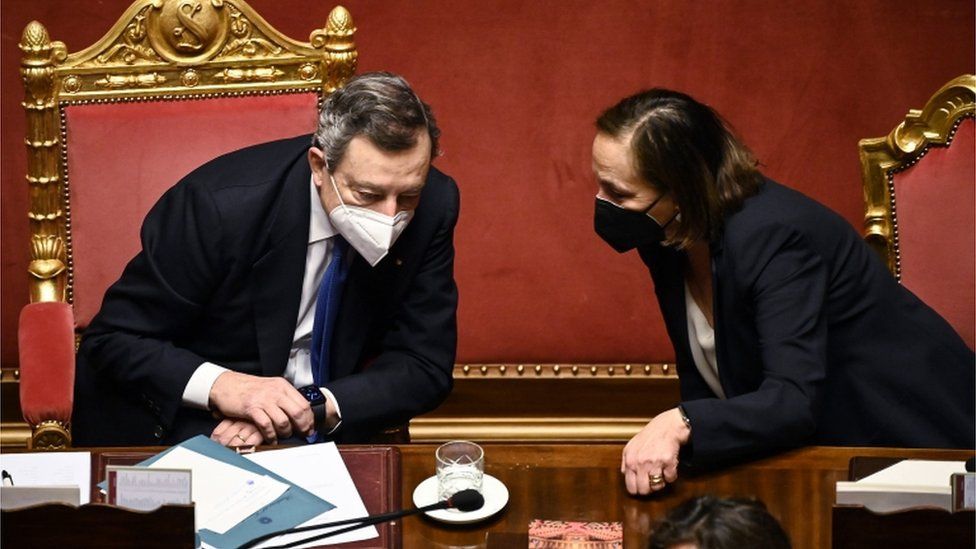

"We must ask pharmaceutical companies to fully respect their commitments on a European level," Mr Draghi said, calling for a supply chain that was not vulnerable to shocks and decisions made elsewhere.
Italy is one of 19 EU countries seeing a rise in Covid infections, according to the EU. Poland has reported a record 29,978 cases in the past 24 hours.
What the Commission is planning
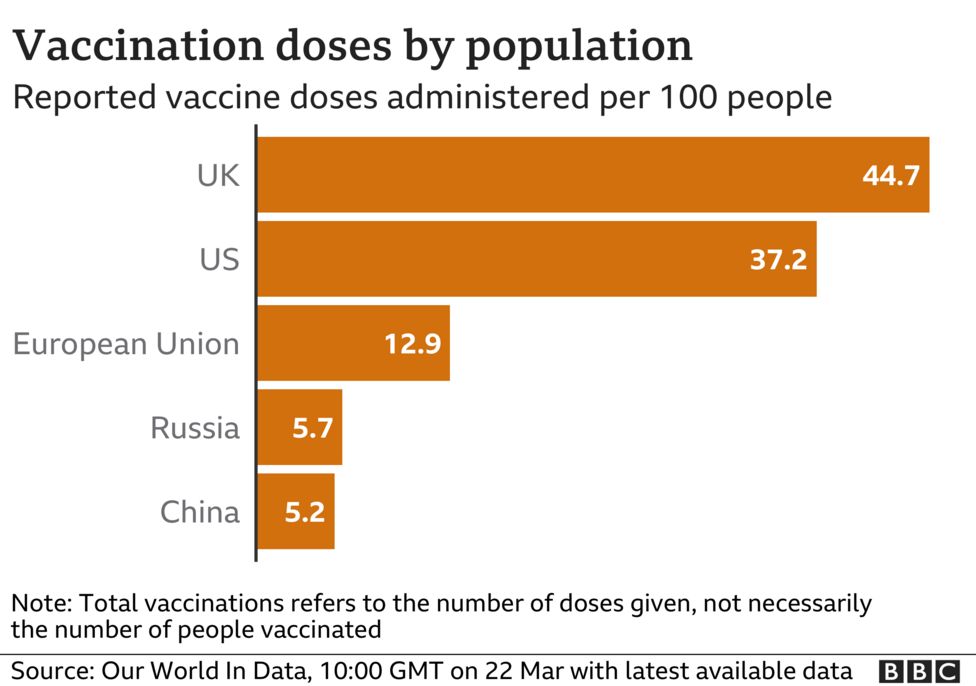
The tougher export controls are most like to affect vaccine-exporting countries that have higher vaccination rates than the EU, such as the UK and US.
The key criteria for the proposed regulations are "reciprocity" and "proportionality":
- The EU says there is no reciprocity if a country importing vaccines from the EU restricts exports itself either by law or other means, so "it may be appropriate to consider whether exports to this country are justified"
- Member states and the Commission will also consider the epidemiological situation in that non-EU country, its vaccination rate and existing availability of Covid-19 vaccines.
There will be no outright export bans, which are opposed by countries such as the Netherlands and Belgium.
Vaccine manufacturers would be assessed to see if they were fulfilling their contract with the EU, although no specific algorithm is planned.
A UK government spokesperson said: "We are all fighting the same pandemic - vaccines are an international operation; they are produced by collaboration by great scientists around the world. And we will continue to work with our European partners to deliver the vaccine rollout."
Last week, European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen complained that the EU had exported more than 10 million doses to the UK but the UK had so far exported none in return.
Her colleagues added that this had to be seen in the context of the EU being both a global Covid hotspot and also the biggest exporter of vaccines. Since the end of January, EU countries have exported 43 million doses of vaccine to 33 countries not subject to export authorisation, they say.
UK sources insist vital components are being sent to the continent, for example for the Pfizer vaccine, and they have emphasised the UK's role in investing early in vaccine development, BBC correspondent Nick Beake reports.
The EU's 27 leaders will assess the proposals at a summit on Thursday, in which US President Joe Biden will also take part via video.
Latest Stories
-
Most Ghanaians are like single-phased wires -Prof. Akosa
22 minutes -
GUBA leads historic Memphis-Ghana Trade Mission, paving the way for diaspora investment
29 minutes -
KNUST declares 2 former students persona non grata over indiscipline, campus disturbances
42 minutes -
IGP clarifies comments on recruitment of Bawku youth into the police service
48 minutes -
GOIL CEO tours Tema Lubes Oil Company
2 hours -
Communication Minister meets Afriwave Telecom management
2 hours -
We cannot remain imprisoned in history and lamentation – Prof. Lumumba urges
3 hours -
Ukraine allies pledge €21bn in fresh military aid
3 hours -
Bawku: IGP’s recruitment comment may be well-intended but timing is bad – Security analyst
3 hours -
We must re-enter 21st century with laws known to Ghana – Prof Lumumba
3 hours -
Minority urges gov’t to take drastic action amid fresh clashes in Bawku
3 hours -
Bosompem Richmond writes: IGP Yohunu’s approach to Bawku conflict dangerous
3 hours -
Bawku crisis: IGP’s recruitment comment out of place – Minority
3 hours -
Lecturers exempted from post-retirement contract ban – Education Minister
3 hours -
U.S. Army Europe Band’s Barbarossa Woodwind Quintet thrills pupils of Ringway Estate Basic School in Accra
4 hours