Installing huge numbers of solar panels and wind turbines in the Sahara desert would have a major impact on rainfall, vegetation and temperatures, researchers say.
They found that the actions of wind turbines would double the amount of rain that would fall in the region.
Solar panels have a similar impact although they act in a different way.
The authors say their work reinforces the view that large-scale renewables could transform the Sahara region.
The scientists modelled what would happen if 9 million sq km of the Sahara desert was covered in renewable energy sources.
They focussed on this area because it is sparsely populated, and it is also exposed to significant amounts of sun and wind and is close to large energy markets in Europe and the Middle East.
According to authors' calculations, a massive installation in the desert would generate more than four times the amount of energy that the world currently uses every year.
Previous studies have shown that installing wind and solar can have an impact on temperatures - but the key difference with this research is the impact on vegetation.
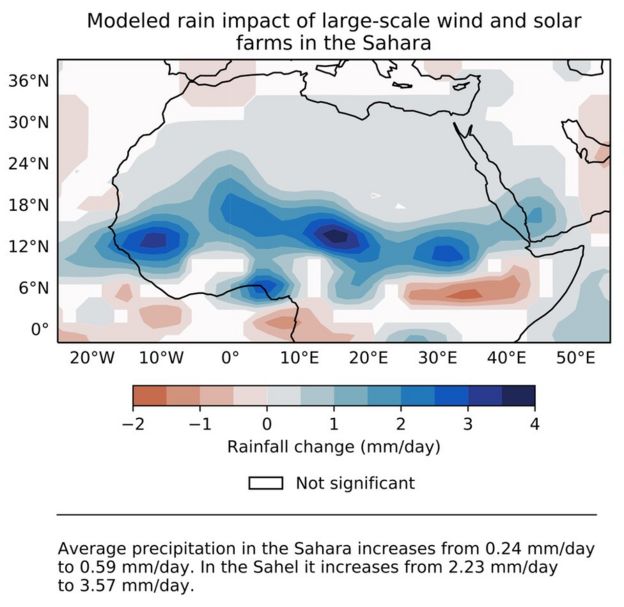
"Our model results show that large-scale solar and wind farms in the Sahara would more than double the precipitation, especially in the Sahel, where the magnitude of rainfall increase is between 20mm and 500mm per year," said Dr Yan Li, the lead author of the paper from the University of Illinois, US.
"As a result, vegetation cover fraction increases by about 20%."
In the Sahel, the semi-arid region that lies to the south of the Sahara, average rainfall increased 1.12mm per day where wind farms were present, according to the study.
How do turbines and panels increase rainfall?
With wind turbines, it's all about the mixing of air caused by the rotation of the blades. Wind farms mix warmer air from above, which creates a feedback loop whereby more evaporation, precipitation and plant growth occurs.
"Wind farms increase surface roughness and therefore increase wind converging into low-pressure areas," said Dr Li. "The converging air has to rise, making it cool off and moisture condense, which will lead to increased rainfall."

Solar panels actually reduce the reflection of sunlight from the surface known as the albedo effect. This triggers a positive albedo-precipitation-vegetation feedback that leads to precipitation increases of about 50%, the authors report.
"The panels directly reduce the surface albedo which leads to more solar energy absorption and surface warming, which in turn strengthens the Saharan heat low, leading to more rising air and precipitation," Dr Li explained.
What would be the impact on people?
Mostly positive, say the authors.
"Precipitation increases predicted by our model would lead to substantial improvements of rain-fed agriculture in the region, and vegetation increases would lead to the growth in production of livestock," said Dr Safa Motesharrei, from the University of Maryland, another author of the paper.
"The Sahara, the Sahel, and the Middle East include some of the driest regions in the world, while experiencing high growth of population and poverty, and our study has major implications for addressing the intertwined sustainability challenges of the energy-water-food nexus in this region."
But temperature rises are bad for climate change, right?
The authors say that the heating impact of all those turbines and panels would not make an important difference.
"The local warming by wind and solar farms is much smaller compared with the reduced future warming from greenhouse gases that renewable power at this scale would imply," said Dr Li.
Will this work with smaller-scale renewable installations?
The authors also looked at other desert locations in different parts of the world but they found the impact on rainfall and vegetation growth was much smaller. They also believe that fewer panels and turbines would have a limited effect.
"Generally, the climate impacts are reduced with reduced installations, but this result depends also very much on the exact locations," said Dr Li.
Should we now proceed with big installations in desert areas?
"Yes, I think so," said Dr Li.
"The main message for people, policymakers, and investors is the enormous benefits to the people, society, and ecosystem as a result of these solar and wind farms."
"We hope that, in the light of our findings, and because of the primary climate effect of these farms is the reduction of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions and the resulting mitigation of climate change, we could transform our energy sources. That can lead in turn to sustaining freshwater, food, and life on our planet."
The study has been published in the journal, Science.
Latest Stories
-
4-year-old cured leper walks again after Bawumia sponsored her special surgery
2 hours -
Dorcas Affo-Toffey, earns dual Master’s Degrees in Energy, Sustainable Management, and Business Administration
3 hours -
T-bills auction: Government got GH¢21.5bn in November 2024, lower than target
6 hours -
Ghana to return to single digit inflation in quarter one 2026
6 hours -
Panama’s president calls Trump’s Chinese canal claim ‘nonsense’
7 hours -
Manmohan Singh, Indian ex-PM and architect of economic reform, dies at 92
7 hours -
Government is not been fair to WAEC – Clement Apaak on delay to release WASSCE results
7 hours -
Bayer Leverkusen’s Jeremie Frimpong donates to Osu Children’s Home in Ghana
10 hours -
GPL 2024/25: Heart of Lions beat Young Apostles to go three points clear
11 hours -
Dance battles, musical chairs light up Joy FM Party in the Park
11 hours -
Kwabena Kwabena, Camidoh, Kwan Pa Band, others rock Joy FM Family Party in the Park
11 hours -
GPL 2024/2025: Aduana beat struggling Legon Cities
11 hours -
GPL 2024/25: Bechem United fail to honor match against Holy Stars
11 hours -
Cooking competition takes centrestage at Joy FM Family Party In The Park
12 hours -
Album review: ‘Wonder’ by Nana Fredua-Agyeman Jnr
14 hours

