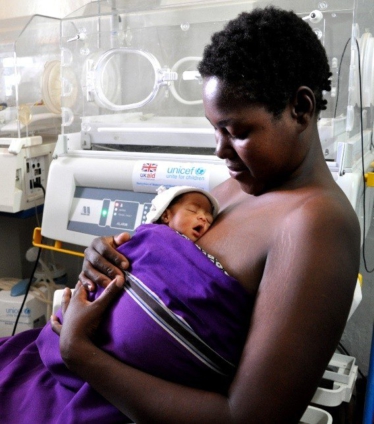
The results of a new clinical trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine, show that immediate kangaroo mother care, which involves skin-to-skin contact with the mother and exclusive breastfeeding, started as soon as a preterm or low birthweight baby is born, dramatically improves survival.
Current World Health Organization (WHO) recommendations indicate starting kangaroo mother care only after the baby is stabilized in an incubator or warmer, which can take on average 3-7 days.
This new study suggests that, when compared with the existing practice, starting kangaroo mother care immediately after birth can save up to 150,000 more lives each year.
“Keeping the mother and baby together right from birth with zero separation will revolutionize the way neonatal intensive care is practiced for babies born early or small,” said Dr Rajiv Bahl, Head of the Newborn Unit at WHO, and the coordinator of the study. “When started at the soonest possible time, kangaroo mother care can save more lives, improve health outcomes for babies and ensures the constant presence of the mother with her sick baby.”
The results of the immediate kangaroo mother care study indicate the need for a global paradigm shift in the care of small babies with zero separation of babies from their mothers by having dedicated Mother-Newborn ICUs. “The best way to nurture the newly born low birthweight baby, including in high-income countries, is through ongoing skin-to-skin contact with the mother, in a mother-newborn couplet care unit that provides care and medical treatment for both,” said Dr Bjorn Westrup, of the Karolinska Institute, Sweden, and a technical expert for the study.
Kangaroo mother care is already known to be effective, reducing mortality by 40% among hospitalized infants with a birth weight less than 2.0 kg when started once they are clinically stable. However, this important new study provides new evidence to show a further 25% reduction when it is initiated immediately after birth, either with the mother or a surrogate.
Dr. Queen Dube, one of the study investigators, and Director of Health Services in Malawi said, “Separating mothers from small and sick newborns adds stress for both mum and baby, at a time when they often both need close contact - immediate Kangaroo Mother Care overcomes this barrier. Keeping the mother and the baby together helps the baby to survive and thrive.
Mother-Newborn ICUs have been established in some countries so that mothers can always be with their babies to provide continuous kangaroo care. Mothers receive their own post-birth care in these wards without being separated from their baby. If a mother is unwell, the selection of a surrogate ensures that the provision of kangaroo care continues until the mother recovers.
During the clinical trial, which was conducted across five countries in Africa and Asia, mothers or surrogates provided approximately 17 hours of skin-to-skin contact per day while in a Mother-Newborn ICU. Delivery of the intervention required close collaboration between obstetric and neonatal departments. It is crucial to note that quality care for all newborns and mothers was provided in the trial which included the provision of respiratory support if required, thermal care, breastfeeding support and prevention and management of infections.
Immediate kangaroo mother care had several other benefits in addition to improved survival. It reduced infections and hypothermia, which are two big killers of small babies. The babies also had more opportunity to breastfeed.
Dr Harish Chellani, one of the study investigators, from Vardhman Mahavir Medical College and Safdarjung Hospital, India, observed, “Health care providers have been separating small and sick babies from their mothers for decades believing that was best for them. The new evidence from this study means we must establish the practice of immediate kangaroo mother care globally”.
WHO is in the process of reviewing its current recommendations on kangaroo mother care, published in 2015, in light of the new evidence that has become available.
About the study
This study was a two arm, randomised controlled trial set in high volume, public tertiary care units in Ghana, India, Malawi, Nigeria and Tanzania.
In Ghana, the School of Public Health, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology and the Komfo Anokye Teaching Hospital colloborated in this study.
The babies in the immediate kangaroo mother care group started the intervention as soon as possible after birth and got an average of 17 hours per day in the Mother-Newborn ICU in the first three days.
In the control group, kangaroo mother care was started only after the baby was stable and the babies got about 1.5 hours per day in the neonatal ICU; both the study groups got kangaroo mother care thereafter (about 19 hours / day).
The study planned to include 4200 infants but was stopped early due to clear evidence of benefit on survival.
Latest Stories
-
Actress Benyiwaa of ‘Efiewura’ TV series dead
21 minutes -
Ashanti Regional Chief Imam dies at age 74
46 minutes -
Africa Arts Network calls for tax reform to save Ghana’s theatre industry
58 minutes -
SSTN Ghana Chapter reaffirms commitment to economic growth under new leadership
1 hour -
Inlaks strengthens leadership team with key appointments to drive growth across sub-Saharan Africa
2 hours -
Green Financing: What Ghana’s Eco-startups need to know
2 hours -
CHAN Qualifiers: Amoah confident of beating Nigeria
2 hours -
Governments deprioritising health spending – WHO
2 hours -
Lordina Foundation brings Christmas joy to orphans
2 hours -
Yvonne Chaka Chaka to headline ‘The African Festival’ this December
2 hours -
Nigerian man promised pardon after 10 years on death row for stealing hens
2 hours -
MGA Foundation deepens support for Potter’s Village
3 hours -
Galamsey: One dead, 3 injured as pit collapses at Nkonteng
3 hours -
Man, 54, charged for beating wife to death with iron rod
3 hours -
MedDropBox donates to UG Medical Centre
4 hours