Audio By Carbonatix
Access to the internet has been restored after it was blocked by Myanmar's new military rulers.
The blackout was the second night in a row and the fourth shutdown since the 1 February coup and came as the junta tries to stifle dissent.
Earlier, the military authorities announced stiff penalties for those opposing the coup leaders.
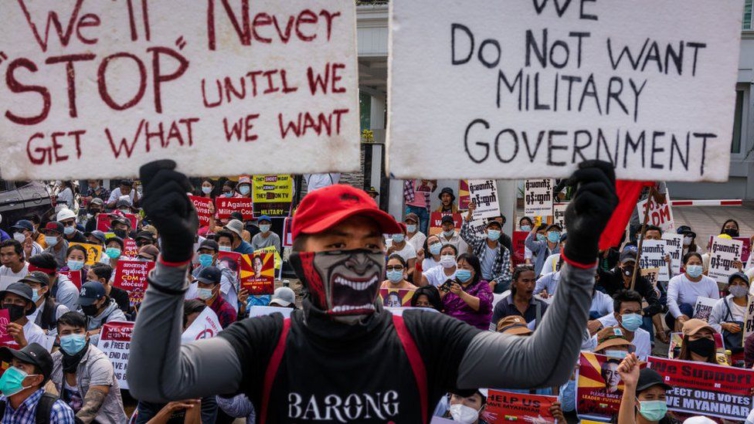
But protesters were out again early on Tuesday, with news agency Reuters reporting small groups gathering.
They have been encouraging civil servants to join the civil disobedience movement in the main city of Yangon.
The United Nations Special Envoy Christine Schraner Burgener reminded the head of the military junta in a phone call that "the right of peaceful assembly must fully be respected", according to a UN spokesman, warning him that "any form of heavy handed response is likely to have severe consequences".
The junta says it overthrew elected leaders, including longtime democracy campaigner, Aung San Suu Kyi, due to alleged voter fraud. It has not provided any evidence to support these claims.
Why are they shutting down the internet?
The latest shutdown follows a pattern aimed at disrupting continuing opposition to the coup and the detention of leaders, including Ms Suu Kyi, whose party won a resounding victory last November.
Access to Facebook, a rallying point for a campaign of civil disobedience, was restricted soon after the coup. Use of Twitter and Instagram was also disrupted.
But activists also fear the blackout may be used to arrest more people.
Major telecoms provider Telenor has said it will no longer be updating a list on its website of internet disruption. It told AFP news agency that the situation was "confused and unclear" and said that employee safety was a "top priority".
What is happening on the streets?
The military's presence is growing. At many strategic locations, soldiers have replaced the police.
In the main city, Yangon, eight-wheeled armoured vehicles have been seen trying to navigate the rush-hour traffic, sometimes surrounded by cars honking in opposition to the coup.
On Monday, protests focused on the central bank building, the US and Chinese embassies, and the city headquarters of Ms Su Kyi's National League for Democracy.
And as demonstrators gathered in the central city of Mandalay, there were reports of security forces firing rubber bullets to disperse crowds.
In footage posted on social media, the sound of what appears to be gunshots can be heard as crowds flee, with several people later appearing to display injuries.
A leading student activist who has gone into hiding, Myo Ko Ko, told the BBC why he and others were willing to risk their lives.
"We strongly believe in democracy and human rights. We know that it's risky," he said.
"I have to move to another place day by day because of being searched (for) by police. We hope the international community will help us."
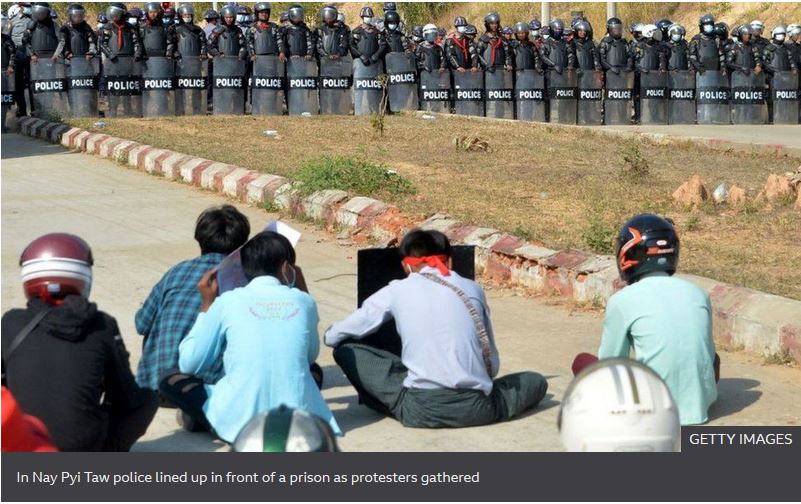

Students also protested in the capital, Nay Pyi Taw. Dozens were arrested and later released.
Residents in several cities are reported to have formed night-watch groups to deter mobs rumoured to have been dispatched by the military to cause unrest.
What are the new punishments protesters face?
The demonstrators are demanding the release from detention of their elected leaders, including Ms Suu Kyi, and the restoration of democracy in Myanmar, also known as Burma.
But the ruling junta has threatened long prison sentences and fines for anyone found to incite hatred towards the military, "by words, either spoken or written, or by signs, or by visible representation".
In a statement posted on a military website on Monday, it said that people preventing the security forces from carrying out their duties could face 20 years in prison, while those found to stir up fear or unrest in public could be imprisoned for terms of three to seven years.
The military government on Saturday gave itself the power to make arrests, carry out searches and hold people for more than 24 hours without a court ruling.
It has also told journalists not to describe the military's takeover as a coup.

Myanmar - the basics
- Myanmar, also known as Burma, was long considered a pariah state while under the rule of an oppressive military junta from 1962 to 2011
- A gradual liberalisation began in 2010, leading to free elections in 2015 and the installation of a government led by veteran opposition leader Aung San Suu Kyi the following year
- In 2017, a deadly crackdown by Myanmar's army on Rohingya Muslims sent more than half a million fleeing across the border into Bangladesh, in what the UN later called a "textbook example of ethnic cleansing"
- Aung San Suu Kyi and her government were overthrown in an army coup on 1 February following a landslide NLD win in November's elections
Latest Stories
-
Firefighters subdue blaze at Accra’s Tudu, officials warn of busy fire season ahead
12 minutes -
New Year’s Luv FM Family Party in the park ends in grand style at Rattray park
17 minutes -
Mahama targets digital schools, universal healthcare, and food self-sufficiency in 2026
24 minutes -
Ghana’s global image boosted by our world-acclaimed reset agenda – Mahama
45 minutes -
Full text: Mahama’s New Year message to the nation
45 minutes -
The foundation is laid; now we accelerate and expand in 2026 – Mahama
1 hour -
There is no NPP, CPP nor NDC Ghana, only one Ghana – Mahama
1 hour -
Eduwatch praises education financing gains but warns delays, teacher gaps could derail reforms
1 hour -
Kusaal Wikimedians take local language online in 14-day digital campaign
2 hours -
Stop interfering in each other’s roles – Bole-Bamboi MP appeals to traditional rulers for peace
2 hours -
Playback: President Mahama addressed the nation in New Year message
3 hours -
Industrial and Commercial Workers’ Union call for strong work ethics, economic participation in 2026 new year message
5 hours -
Crossover Joy: Churches in Ghana welcome 2026 with fire and faith
5 hours -
Traffic chaos on Accra–Kumasi Highway leaves hundreds stranded as diversions gridlock
5 hours -
Luv FM Family Party in the Park: Hundreds of families flock to Luv FM family party as more join the queue in excitement
5 hours

