On 2nd July, 2020, a Singaporean vessel-KOTA BODI was boarded by a group of armed men 153nm miles of the coast of Cotonou and 5 crewmembers aboard the vessel were kidnapped.
A few weeks later, 13 people were kidnapped after another vessel-MT CURCACAO TRADER was attacked by pirates 244nm away from Cotonou coast. These incidents are amongst the several numbers of pirate attacks that have been reported in the Gulf of Guinea in the last 9 months. The 3500 miles stretch territory of has overtaken the Horn of Africa as the hub of piracy in the world.
According to the International Maritime Bureau (IMB), 90% of global maritime kidnappings in 2019 was recorded in the Gulf of Guinea despite the reduction in global pirate activities.
Prevalence of Piracy at West African Coasts
Global pirate activities are currently on the rise after being on a decline in the last few years.
According to the IMB’s Piracy Reporting Centre (PRC), 98 incidents of piracy and armed robbery were recorded in the first half of 2020, an increase from 78 in Quarter 2 of 2019. Allianz also reports that about 45% of global piracy occurred in the Gulf of Guinea in the first quarter of 2020 most of which targeted bunker (oil) carriers, fishing vessels and container ships.
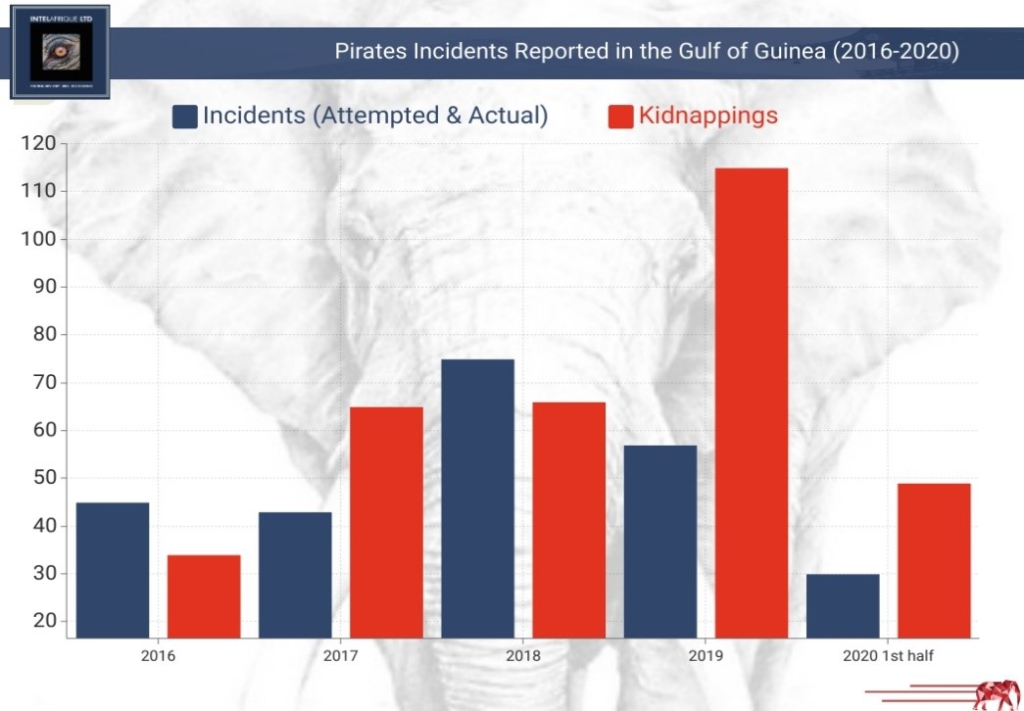
This increasing threats of piracy in the region add to the difficulties faced by sea fearers who are operating beyond their contracts due to COVID-19 restrictions on vessel activities - crew rotations and international travel.
Vessels, particularly crew members, are extremely vulnerable to attacks as pirates now favour kidnapping crewmembers for ransom instead of stealing and oil bunkering. Since the beginning of the year, about 49 seafarers have been kidnapped in the Gulf of Guinea majority of which were located in the waters of West African countries—Nigeria, Benin, Togo and Ghana.
Rates of abduction accelerated in the 2nd quarter of 2020 with as 32 out of the 49 kidnappings. On some occasions, kidnapping hostages provide some leverage during negotiations with government authorities.
The location of attacks is another issue that has rasied concerns in the region. Incidents are now occurring further off the coast. Two-thirds of the attacks on vessels were on the high seas from around 20 to 130 nautical miles off the Gulf of Guinea coastline.
The trend could be attributed to the inadequate presence of security patrols in the high seas making pirates more confident and comfortable to engage vessels in the high seas. These bandits have also become well-equipped (armed) to enable them to reach vessels as far as 130-150 nautical miles offshore.
Criminal networks—motivated by profits also have a huge presence in the Gulf. Criminal activities in the Gulf ranges from petty thieves/armed robbers to organised pirate establishments. Politically motivated attacks have also been experienced in the region.
Insurgent groups such as the Movement for the Emancipation of the Delta (MEND) and the Niger Delta Avengers (NDA) have had political and environmental disputes with large oil multinational companies in the Niger Delta; and have been accused by authorities of having connections with pirate activities in the region—Niger Delta.
These networks mostly originated from the Niger Delta area but have expanded their operations into other parts of the region and waters off Togo, Ghana, Benin, and Cameroun.
Apart from the insecurity faced by travelling vessels, foreign investments is at risk as the Guf of Guinea’s reputation as a high-risk maritime trade route discourages economic activity and increases insurance costs particulary in reference to Kidnap and ransom which adversely affects both the public and private secotor growth.

Several counterpiracy mechanisms have been implemented in the region over the last decade and have made some significant progress—improving information sharing among authorities. In 2016, under the Yaounde Code of Conduct, 6 countries in the region carried out a coordinated information-sharing network that assisted the Nigerian Navy located and rescue hostages that were kidnapped from the vessel—MT Maximus off the coast of Cote d’ Ivoire.
Despite, such progress, more work is required especially to align counterpiracy efforts with the political and socio-economic reforms of respective coastal West African countries. Counter piracy efforts should not only focus on prosecuting culprits of maritime crime but should be holistic and include efforts that will also address the socio-economic, political and even environmental grievances that fuels piracy in the region.
-
IntelAfrique is a unique partnership of highly experienced young professionals offering a diverse skills set and astute knowledge of the West African sub-region.
Latest Stories
-
IPR Ghana congratulates citizens for peaceful election, calls for unity
3 minutes -
Bawumia’s 8 minutes elite ball that zapped the energy of trigger happy politicians
52 minutes -
It will be a betrayal if National Cathedral saga does not feature in ORAL’s work – Ablakwa
1 hour -
‘It’s unfortunate we had to protect the public purse from Akufo-Addo’ – Ablakwa on ORAL Team’s mission
2 hours -
Congo lawyers say Apple’s supply chain statement must be verified
2 hours -
Stampede in southwestern Nigerian city causes multiple deaths
3 hours -
Tens of thousands without water in Mayotte as curfew brought in
3 hours -
ORAL: We won’t witch-hunt, we’ll focus on transparency, not revenge – Ablakwa
3 hours -
Attempted robbery: Accused claims he carried cutlass for protection
3 hours -
Excavator operator jailed for stealing
4 hours -
African fans age-shame me for putting on some outfits – Tiwa Savage
4 hours -
Tiwa Savage criticised by female fans for stance on cheating in relationships
4 hours -
Bank of England expected to hold interest rates
4 hours -
Congo river boat sinks killing at least 22
5 hours -
Nigeria approves Shell’s $2.4 billion asset sale to Renaissance
5 hours
